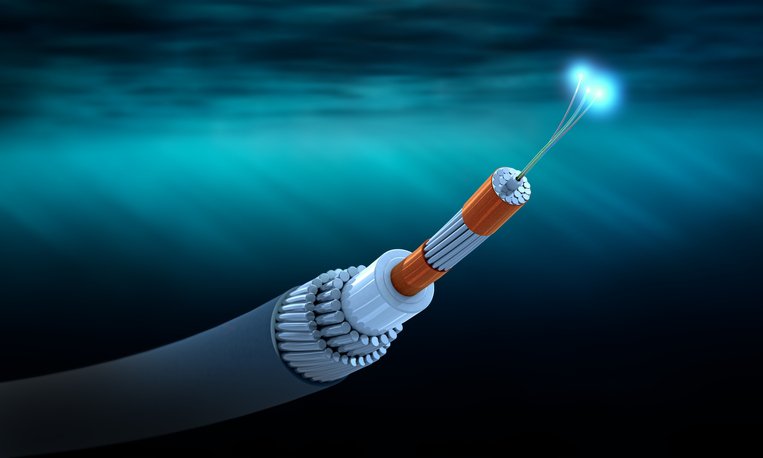
Underwater cables, also known as submarine cables, are vital components of modern communication networks, facilitating the transmission of data and power across vast distances beneath the world’s oceans. From enabling high-speed internet connectivity to supporting international telecommunications, these cables play a crucial role in connecting people and businesses globally.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Underwater Cables
Underwater cables are intricate systems of fiber optic strands and protective layers designed to withstand the harsh conditions of the ocean floor while ensuring seamless data transmission. They serve as the backbone of global communication networks, allowing for the exchange of information between continents in milliseconds.
What are underwater Cables?
Underwater cables are long, flexible strands of fiber optics encased in protective layers, designed to transmit data signals across vast distances underwater. They are laid on the seabed to establish communication links between different regions of the world.
Importance of Underwater Cables in Modern Communication
In an increasingly interconnected world, underwater cables are essential for facilitating global communication, enabling instant access to information, and supporting various industries such as finance, healthcare, and entertainment.
History of Underwater Cables
The history of underwater cables dates back to the mid-19th century when the first transatlantic telegraph cable was laid across the Atlantic Ocean. Since then, there have been significant advancements in underwater cable technology, leading to the development of high-capacity fiber optic cables that can transmit vast amounts of data at incredible speeds.
Early Developments in Underwater Cable Technology
The early underwater cables were simple copper wires insulated with gutta-percha, a type of natural rubber. While these cables revolutionized long-distance communication, they were prone to damage and had limited bandwidth.
Milestones in the History of Underwater cables
The laying of the first transatlantic telegraph cable in 1858 marked a significant milestone in underwater cable technology, reducing the time it took to communicate between Europe and North America from weeks to minutes. Since then, there have been numerous advancements in cable design and laying techniques, making underwater cables more reliable and efficient.
Types of Underwater Cables
Underwater cables come in various types, each serving specific purposes depending on the application and requirements.
Submarine Communication Cables
Submarine communication cables are designed to transmit data signals over long distances, connecting continents and enabling global telecommunications. These cables use fiber optic technology to achieve high-speed data transmission rates.
Submarine Power Cables
Submarine power cables are used to transmit electrical power between offshore installations, such as offshore wind farms and mainland power grids. These cables are essential for delivering renewable energy from offshore sources to populated areas.
Components of Underwater Cables
Underwater cables consist of several key components that work together to ensure reliable data transmission and protection against external factors.
Fiber Optic Strands
The core of underwater cables consists of multiple strands of fiber optics, which carry data signals in the form of light pulses. Fiber optic technology allows for high-speed data transmission over long distances without signal degradation.
Protective layers
Underwater cables are encased in multiple layers of protective materials, including insulation, strength members, and water-blocking compounds, to shield them from physical damage and corrosion caused by seawater.
Armoring
Some underwater cables are reinforced with armoring, such as steel wires or metal tapes, to provide additional protection against external threats, including anchor strikes and marine life.
Installation Process
The installation of underwater cables is a complex and highly specialized process that requires careful planning and execution to ensure the cables are laid safely and securely on the seabed.
Cable laying ships
Underwater cables are typically laid using specialized cable laying ships equipped with dynamic positioning systems and cable-laying machinery. These ships follow predetermined routes and use precision navigation techniques to lay the cables on the seabed.
Challenges in underwater cable installation
The installation of underwater cables poses several challenges, including navigating through rough seas, avoiding underwater obstacles, and dealing with unpredictable weather conditions. Additionally, the cables must be laid with precision to avoid damage and ensure optimal performance.
Benefits of Underwater Cables
Underwater cables offer several benefits compared to alternative communication technologies, making them the preferred choice for long-distance data transmission.
High-speed data transmission
Underwater cables can transmit data at speeds of up to several terabits per second, allowing for rapid exchange of information between distant locations.
Reliable connectivity
Unlike wireless communication technologies, which are susceptible to interference and signal loss, underwater cables provide a reliable and stable connection, even in adverse weather conditions.
Applications of Underwater Cables
Underwater cables have a wide range of applications across various industries, including telecommunications, internet connectivity, and renewable energy.
Telecommunications
Underwater cables form the backbone of global telecommunications networks, enabling the transmission of voice, data, and video signals between continents.
Internet Connectivity
Underwater cables are essential for providing high-speed internet connectivity to remote and underserved areas, bridging the digital divide and enabling economic development.
Environmental Impact
The installation and operation of underwater cables can have both positive and negative impacts on the marine environment, depending on various factors such as cable design, installation techniques, and maintenance practices.
Concerns about marine life
One of the primary concerns regarding underwater cables is their potential impact on marine life, including disruption of habitats, entanglement of marine animals, and introduction of pollutants into the ecosystem.
Mitigation measures
To mitigate the environmental impact of underwater cables, various measures can be implemented, such as selecting cable routes that avoid sensitive habitats, using eco-friendly materials, and conducting environmental impact assessments prior to installation.
Maintenance and Repair
Regular maintenance and timely repair of underwater cables are essential for ensuring their continued operation and reliability.
Monitoring systems
Underwater cables are equipped with monitoring systems that allow operators to detect faults and anomalies in real-time, enabling proactive maintenance and swift response to any issues that may arise.
Techniques for repairing underwater cables
In the event of cable damage or malfunction, specialized repair ships and remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) are deployed to locate and repair the affected sections of the cable, ensuring minimal disruption to communication services.
Future Trends
The future of underwater cables is characterized by continued advancements in technology and expansion of global connectivity.
Advancements in cable technology
Research and development efforts are focused on enhancing the capacity and efficiency of underwater cables, with innovations such as higher-density fiber optic cables and improved signal processing techniques.
Expansion of underwater cable networks
As demand for high-speed internet and reliable communication continues to grow, there is a trend towards expanding underwater cable networks to new regions and increasing the capacity of existing routes.
Security Considerations
Ensuring the security of underwater cables is paramount to safeguarding global communication networks against physical and cyber threats.
Protection against physical damage
Underwater cables are protected against physical damage by employing robust construction techniques, implementing security measures to deter sabotage and vandalism, and closely monitoring cable routes for any suspicious activity.
Cybersecurity threats
With the increasing reliance on digital communication, cybersecurity threats pose a significant risk to underwater cables, necessitating the implementation of encryption protocols, intrusion detection systems, and other cybersecurity measures to protect against data breaches and cyber attacks.
Cost Factors
The cost of deploying and maintaining underwater cables varies depending on various factors such as cable length, depth, and complexity of installation.
Initial investment
The initial investment required for laying underwater cables can be substantial, including costs associated with cable manufacturing, cable laying ships, and surveying and permitting.
Long-term maintenance costs
In addition to the initial investment, there are ongoing maintenance costs associated with monitoring, repairing, and replacing underwater cables over their operational lifespan, which can span several decades.
Regulatory Framework
The deployment and operation of underwater cables are subject to various international agreements and government regulations to ensure safety, security, and environmental protection.
International agreements
International agreements such as the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) govern the use of the ocean and establish rules and guidelines for the laying and maintenance of underwater cables in international waters.
Government regulations
Individual countries also have their own regulations and permitting requirements governing the installation and operation of underwater cables within their territorial waters, including environmental impact assessments and marine spatial planning.
Case Studies
Several successful underwater cable projects serve as examples of the benefits and challenges associated with deploying and maintaining submarine cables.
Successful underwater cable projects
Projects such as the Transatlantic Telegraph Cable and the Asia-America Gateway have demonstrated the importance of underwater cables in facilitating global communication and economic development.
Challenges faced in specific regions
Challenges such as geopolitical tensions, natural disasters, and maritime hazards can pose significant obstacles to underwater cable projects in certain regions, highlighting the need for careful planning and risk management.
Conclusion
Underwater cables are indispensable components of modern communication networks, enabling global connectivity and supporting various industries and applications. Despite the challenges and environmental concerns associated with their deployment and operation, underwater cables continue to play a vital role in connecting people and businesses around the world.
FAQs:
How are underwater cables laid on the seabed?
Underwater cables are laid using specialized cable laying ships equipped with dynamic positioning systems and cable-laying machinery. These ships follow predetermined routes and use precision navigation techniques to lay the cables on the seabed.
What are the main environmental concerns associated with underwater cables?
The main environmental concerns associated with underwater cables include disruption of marine habitats, entanglement of marine animals, and introduction of pollutants into the ecosystem.
How do underwater cables transmit data across long distances?
Underwater cables transmit data using fiber optic technology, which involves sending light pulses through fiber optic strands encased in protective layers. This allows for high-speed data transmission with minimal signal degradation.
What measures are taken to protect underwater cables against physical and cyber threats?
Underwater cables are protected against physical threats by employing robust construction techniques, implementing security measures to deter sabotage and vandalism, and closely monitoring cable routes for any suspicious activity. Cybersecurity measures, such as encryption protocols and intrusion detection systems, are also implemented to protect against cyber threats.
What are some of the future trends in underwater cable technology?
Future trends in underwater cable technology include advancements in cable design and manufacturing, increased capacity and efficiency, and expansion of global cable networks to new regions.